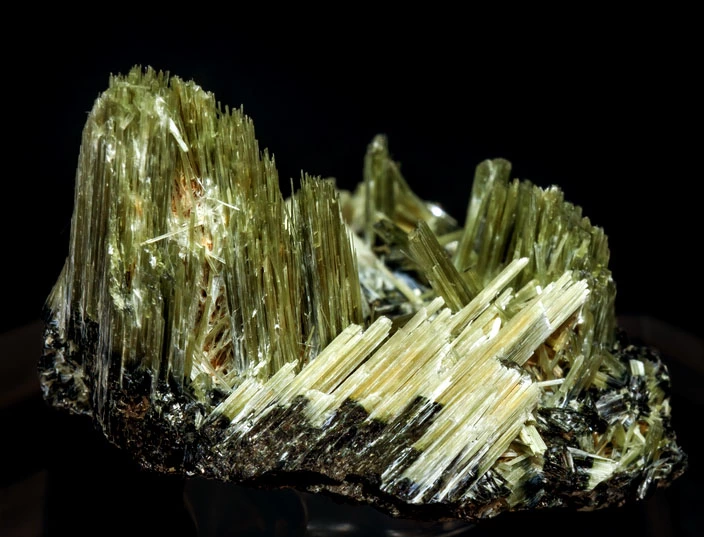
Definition: Actinolite gets its name from the Greek word “aktis”, which means “beam” or “ray”. The amphibole family includes actinolite, which is a common mineral. It develops when mafic igneous rocks or carbonate-rich rocks like limey mudstones undergo low-grade metamorphism. Actinolite can be found in Quartz crystals as thin, splintery inclusions. Chatoyancy in Quartz occurs when the inclusions are parallel and dense. Actinolite crystallizes seldom. Radiating fibrous to asbestiform masses are the most typical manifestations. It may also be found as bladed crystals up to 15 cm in length; columnar, Crystals can be twisted or kinked. A crystal is a kind of substance in which the atoms, molecules, or ions are organized in a three-dimensional lattice that is highly ordered.
Value: The mineral actinolite belongs to a group of minerals that include different proportions of iron and magnesium. The Mg end is tremolite, and the Fe end is ferro-actinolite, with actinolite in the center. Actinolites with more than 50% Fe are extremely uncommon. Actinolite is a bad jewelry stone because it is simple to cleave but difficult to cut. The main component of nephrite is actinolite (jade).
Use: Many other products, notably those containing talc and vermiculite, include actinolite as a contaminant. Actinolite is a trace contaminant that can be found in mineral-rich paints, sealants, fireproofing goods, concrete products, gardening soils, and other items.
Common Products made with Actinolite Asbestos:
- Vermiculite-based structural fireproofing materials
- Concrete with asbestos
- Children’s toys
- Drywall
- Sealants
- Talcum powder
- Vermiculite loose-fill attic insulation
Actinolite is used as a gemstone in some forms. One of the two varieties of jade is nephrite. The chatoyant variant of actinolite known as cat’s-eye actinolite is another gem variation. The hue of this stone ranges from translucent to opaque, and it is green to yellowish-green in appearance. The common name for this type is jade cat’s-eye. Transparent actinolite is a gem collector’s favorite since it’s uncommon and faceted. Taiwan and Canada are the primary suppliers of various types of actinolite. Madagascar, Tanzania, and the United States are among the other sources.

Characteristics of Actinolite:
- Category is Inosilicates
- Group is Amphibole
- Formula is Ca2(Mg4.5-2.5Fe2+0.5-2.5) Si8O22(OH)2
- Color is usually pale to dark green, white or gray, yellowish green and black.
- Luster is vitreous to dull.
- Diaphaneity is translucent to transparent.
- Crystal System is monoclinic
- Crystal Class isPrismatic (2/m)
- Crystal Habits: bladed, fibrous, radial
- Cleavage: is perfect in two directions at close to 60- and 110-degree angles.
- Fracture is splintery to uneven.
- Hardness is 5 – 6.
- Specific Gravity is 3.00
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals are quartz, lawsonite, epidote and glaucophane.
- Other Characteristics: the compact nephrite type is highly strong, even tougher than steel.
- Notable Occurrences include the Lake Baikal Region, Russia; China; New Zealand; British Columbia, Canada, Taiwan, Madagascar, Tanzania, and the United States.
Actinolite is a relatively common crystal that may be found in many different places across the world. Actinolite comes in two extremely uncommon forms, both of which are highly sought after by collectors and practitioners.