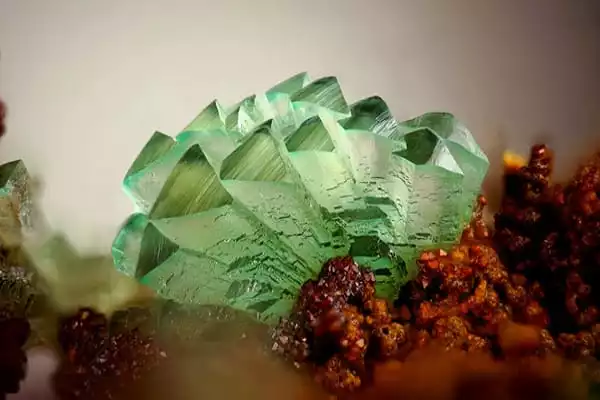
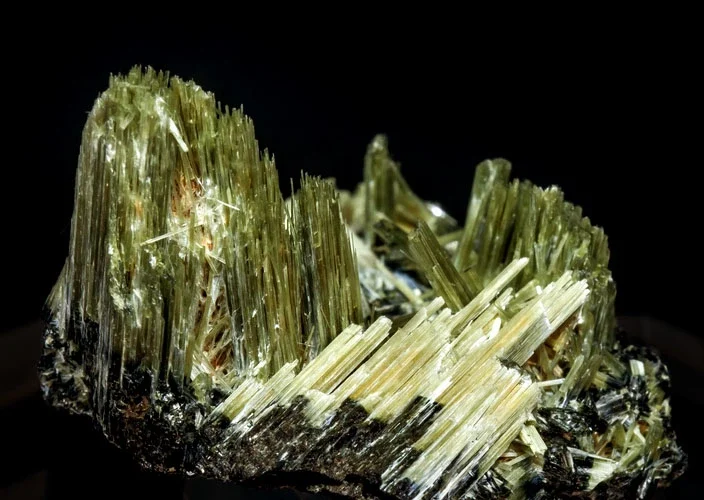
Description
Aegirine belongs to the pyroxene group and is found in a series with the mineral Augite. It is well recognized for its long, thin crystals with characteristic terminations, and some of the most lustrous varieties are truly classics. Hans Morten Thrane Esmark (1801–1882), a Norwegian mineralogist, named aegirine. In honor of the finding of Aegirine near the sea, Esmark named this mineral after Aegir, a mythological Norse sea deity.
Aegirine is renowned as a stone that helps us to “see the light”—for some, this might mean finding our way out of a low emotional condition, while for others, it can signify a burst of energy or unexpected insight. Aegirine is the conqueror of darkness in every aspect.
General Aegirine Information
| Category | Silicate mineral, pyroxene |
| Chemical Formula | NaFe+++Si2O6 |
| Crystal class | Prismatic (2/m) |
| Locality | Norway, Buskerud, Kongsberg. Magnet Cove, Hot Spring County, Arkansas |
| Synonym | Acmite |
Identification Information
| Colour | Green, Greenish Black, Reddish brown, Black. |
| Fracture | Uneven |
| Tenacity | Brittle |
| Hardness | 6-6.5 – Orthoclase-Pyrite |
| Luster | Vitreous to slightly resinous |
| Luminescence | Non-fluorescent |
| Specific gravity | 3.50 – 3.60 |
Meaning and Energy
Aegirine is a powerful stone with a high vibrational frequency. It assists in cleaning and guarding, especially when bad energy is present. It is a stone of confidence and will benefit anyone who is lacking in self-love and admiration. By assisting you in realizing how powerful you actually are, you will be able to draw wonderful energy that you may not have recognized was even present.
Aegirine is a therapeutic stone that will boost one’s mental health significantly. It will help you break free from monotonous daily routines that are packed with negativity and drive you to focus on yourself. Aegirine will bring forth the power from deep inside that may have been buried behind internal imbalances for anyone battling with addiction of any kind.
Aegirine Physical Healing Energy
Aegirine helps the body digest and eliminate pollutants while also boosting the immunological, metabolic, and neurological systems. It is very beneficial to the liver, spleen, and gallbladder. It is a wonderful gemstone for increasing physical vitality and stamina, as well as for healing after illness or injury. Aegirine protects the nerves, muscles, and bones and can help with muscular discomfort and backaches. Aegirine is a useful stone in Reiki and other energy-transfer healing modalities that rely on the power of touch.

Aegirine Emotional Healing Energy
By breaking negative emotional patterns and attitudes created by blame, shame, guilt, worthlessness, or self-pity, Aegirine can help you overcome sadness, despair, or hopelessness. It helps to repair the emotional body by generating good ideas to replace harmful ones and allowing acceptance of what cannot be altered as well as acceptance of oneself and others as they are.
Aegirine aids in the mending of broken relationships and the transformation of grief following betrayal, separation, or death.
Meditation with Aegirine
Aegirine revitalizes and restores the body. It permits light and love to easily flow throughout the body, eliminating any obstacles in the way. It is a stone of detoxification and recuperation, allowing for long-term benefits and continuous improvements.
Aegirine blades are great for body layouts, guiding energy flow, and removing obstructions while also healing gaps in the aura. For more direct applications, blades can also be used as a wand. Matrix specimens may be held during meditation and are especially beneficial for inner-child work and mood enhancement.